
The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is required in the secretory pathway.
Colley NJ, Baker EK, Stamnes MA, Zuker CS. How are substrates recognized by the ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic system? Trends Biochem Sci. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. The mitochondrial chaperonin hsp60 is required for its own assembly. The ATPase core of a clathrin uncoating protein. Chappell TG, Konforti BB, Schmid SL, Rothman JE. Farnesylation of YDJ1p is required for function at elevated growth temperatures in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Caplan AJ, Tsai J, Casey PJ, Douglas MG. Characterization of YDJ1: a yeast homologue of the bacterial dnaJ protein. YDJ1p facilitates polypeptide translocation across different intracellular membranes by a conserved mechanism. Antifungal properties of the immunosuppressant FK-506: identification of an FK-506-responsive yeast gene distinct from FKB1. Brizuela L, Chrebet G, Bostian KA, Parent SA. Evidence that the 90-kDa heat shock protein is necessary for the steroid binding conformation of the L cell glucocorticoid receptor. Bresnick EH, Dalman FC, Sanchez ER, Pratt WB. hsp82 is an essential protein that is required in higher concentrations for growth of cells at higher temperatures. Borkovich KA, Farrelly FW, Finkelstein DB, Taulien J, Lindquist S. Structure and regulation of the SSA4 HSP70 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Transcriptional regulation of SSA3, an HSP70 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. A homologue of the bacterial heat-shock gene DnaJ that alters protein sorting in yeast. Location of the polypeptides within ribosomes. Controlled proteolysis of nascent polypeptides in rat liver cell fractions. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. MAS5, a yeast homolog of DnaJ involved in mitochondrial protein import. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (2.7M), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. Chaperone proteins induced by heat shock full#
Full textįull text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. In this review, results of experiments are discussed within the context of experiments with other organisms in an attempt to describe the current state of understanding of these ubiquitous and important proteins. The budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has proven very useful in the analysis of the role of molecular chaperones in protein maturation, translocation, and degradation. Several components of this system, encoded by heat-inducible genes, are responsible for the degradation of abnormal or misfolded proteins.
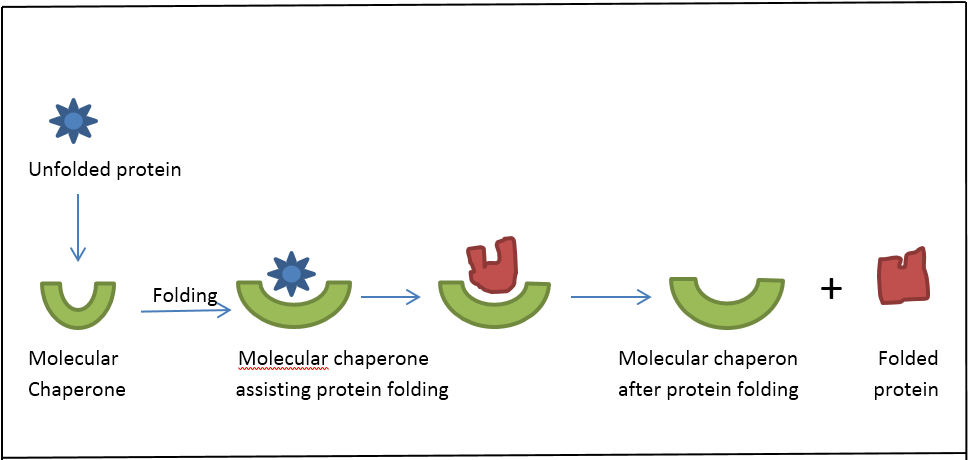
The function of the proteolytic system is intertwined with that of molecular chaperones. Although less well defined, other Hsps such as Hsp90 also play important roles in modulating the activity of a number of proteins. Hsp60 also binds to unfolded proteins, preventing aggregation and facilitating protein folding. Hsp70s interact with incompletely folded proteins, such as nascent chains on ribosomes and proteins in the process of translocation from the cytosol into mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. As a reflection of this role, these Hsps have been referred to as molecular chaperones. Recently, several of the major Hsps have been shown to be intimately involved in protein biogenesis through a direct interaction with a wide variety of proteins. Heat shock proteins (Hsps) were first identified as proteins whose synthesis was enhanced by stresses such as an increase in temperature.





 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
